Have you ever wondered why AI risk management bills are being created?
The short answer is that AI risk management bills create frameworks that help us maximize AI’s positive aspects and minimize its negative aspects.
The long answer?
That’s what this article is about.
AI can do so many amazing things. At the same time, Elon Musk thinks it can also be a “threat to humanity.”
So, how can we find a balance?
Find out in this article by discovering what AI risk management is, several well-known AI risk management frameworks, how AI is applied to risk management, and some examples of AI risk management tools.
Let’s examine the specifics.
What is AI Risk Management?
AI risk management talks about all the processes involved in recognizing, assessing, and mitigating the risks associated with the application of artificial intelligence (AI) technologies.
It’s about creating a standard approach to AI development, deployment, and use so that we maximize AI’s potential and minimize its numerous dangers and risks. These risks include prejudice, discrimination, invasion of privacy, job losses, and many more. Despite these clear worries, AI use is still rising across industries. According to a McKinsey survey, it reached 72% in 2024.
As a result, businesses must minimize AI’s drawbacks while maximizing its benefits. This is accomplished using a set of tools, methods, and systems called AI Risk Management.
The Legislative Response: Popular AI Risk Management Frameworks
In response to the numerous AI risks and threats, the following are some AI risk management frameworks created by different regulatory bodies and government agencies.
1. National Institute of Standard and Technology (NIST) AI Risk Management Framework (AI RMF)
The AI RMF was published in January 2023 by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). It provides organizations with a structured method for managing the risks associated with implementing AI systems in their daily operations.
AI RMF sets out to achieve this objective using four main features. Their details are provided in the table below.
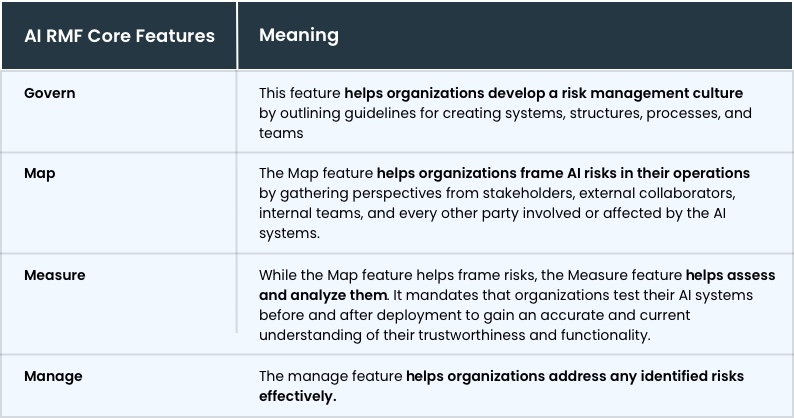
The AI RMF further specifies that reliable AI systems must be safe, accountable, secure, transparent, and fair. To implement these systems, the NIST AI RMF intends to use the core features detailed in the table above. In general, by highlighting these principles, the NIST AI RMF aims to reduce possible risks to people and society while promoting public confidence in AI technologies.
2. The EU AI Act
The European Union (EU) Artificial Intelligence (AI) Act represents the first comprehensive legal framework for governing artificial intelligence (AI) in the European Union. It follows in the footsteps of the EU’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), which was established in 2018. It was passed in order to guarantee the ethical and safe implementation of AI technologies.
This Act uses a risk-based methodology, classifying AI applications into three categories, namely:
- Minimum risk: These include generative AI tools like ChatGPT, which only require transparency and will be mostly unregulated.
- High risk: These are AI systems such as CV-scanning tools for ranking job applicants that can negatively affect safety and fundamental rights. This category of AI systems is subjected to specific legal requirements.
- Unacceptable risk: These AI systems are considered threats to people and should be banned.
The EU AI Act uses these categorizations to protect public safety and basic rights while promoting innovation. It also creates explicit duties for AI developers and implementers, encouraging openness and responsibility. Most importantly, it aims to become a global gold standard for maintaining compliance in AI systems, like the GDPR.
3. Blueprint for the AI Bill of Rights
While it may not be an entirely established AI Bill, the Blueprint for the AI Bill of Rights does provide some guiding principles to govern the design, use, and deployment of AI systems. These principles were formulated to protect Americans from the negative impacts of AI. More specifically, they aim to guarantee that automated systems are created and implemented in a way that respects civil rights and advances equity.
The five principles outlined in the Blueprint for the AI Bill of Rights are:
- Safe and Effective Systems: Before any automated system is deployed for public use, it must undergo a series of safety and effectiveness tests and be monitored on an ongoing basis to mitigate any risks that may arise.
- Algorithmic Discrimination Protections: All AI systems should be designed to prevent discrimination based on race, gender, or other biases. This will ensure fair treatment across the board.
- Data Privacy: AI systems must have safeguards in place to ensure that people are in charge of their personal information.
- Notice and Explanation: Organizations deploying AI systems must ensure that users know when automated systems are being used and how they impact results.
- Human Alternatives: Users must have the option of dealing with human agents as alternatives if they’re not okay with AI systems. It mustn’t be by force.
Even though it is a non-binding guideline, this blueprint still influences policy decisions on the deployment of AI. They ensure that technology is in line with democratic principles and civil rights.
How is AI Used in Risk Management?
While AI risk management practices help ensure that AI systems are safe for organizations, AI models can also help organizations identify potential threats to their businesses.
AI systems are capable of running predictive analytics and providing data-driven insights that allow an organization to foresee potential risks so that they can squash them immediately. In simple terms, AI is being used in risk management across different fields. Below, we’ll highlight some of these use cases. But first, let’s discuss why AI flourishes in risk management.
The following are some unique benefits of AI in risk management:
- AI and ML models are capable of capturing non-linear effects between the variables of a scenario and its risk factor. As a result, it offers a higher forecasting ability than traditional regression systems.
- AI can process large datasets in less time compared to humans or other traditional risk models.
- AI and ML models have superior segmentation skills.
As a result of these capabilities, AI is used in the following risk management use cases:
- Fraud detection and prevention in financial services: AI-enabled fraud detection systems help banks and financial institutions stay ahead of scammers and fraudulent actors by accurately monitoring transactions. They eliminate the risks of financial fraud through their accurate predictive analytics and forecasting capabilities.
- Drug safety: AI’s ability to analyze large datasets accurately makes it easy for the pharmaceutical industry to make drugs safer during production. By analyzing patient data, it helps identify potential drug reactions early.
- Cybersecurity threat detection: AI systems’ ability to quickly spot unusual patterns in network traffic and other relevant data makes it easy to identify potential network breaches, malware, and ransomware signatures.
- Credit risk modeling: Banks and other financial services can also use AI models to evaluate loan applications and spot responsible borrowers by analyzing all their financial data.
- Trader behavior: Regulatory bodies are also leveraging AI’s ability to monitor multiple parameters and variables in a trader’s financial information to detect suspicious activities such as rogue trading, insider trading, and trader misconduct. They monitor differentials like check-in/check-out times, portfolio data, email traffic, call times, etc.
These and many others are some of the ways AI is being used in risk management.
Examples of AI Risk Management Tools
To facilitate the efficient and effective use of AI in the use cases above, the following are some examples of AI risk management tools:
- RiskWatch: For comprehensive risk assessment and compliance management.
- Darktrace: For detecting anomalies and other kinds of cyber threats.
- Riskified: For fraud detection in e-commerce systems.
- CyberGRX: For cyber and third-party risk assessment and management.
- Quantifind: For financial crime detection and data-driven insights.
Conclusion: Implement Compliant AI Systems With Debut Infotech
From the AI Risk Management Framework by NIST to the EU AI Act and the Blueprint for the AI Bill of Rights by the United States, multiple regulatory bodies and government agencies are developing frameworks to govern the creation and implementation of AI systems. Regardless of the semantics used in these bills, their focus remains on creating systems that are fair, secure, and safe for human use.
As such, it is important to maintain compliance with these frameworks if you’re looking to build responsible AI systems. Having been in the AI space long enough, Debut Infotech, an AI development company has all the expertise required to tap into the responsible future of AI. If you’re struggling with the requirements, terminologies, or technicalities required to build these systems, they simply know what to do.
Reach out to them today to be a part of the future of AI.
Caroline is doing her graduation in IT from the University of South California but keens to work as a freelance blogger. She loves to write on the latest information about IoT, technology, and business. She has innovative ideas and shares her experience with her readers.






